How to Calculate a Company’s Weighted Average Number of Outstanding Shares The Motley Fool
Suppose that Sample Company had 100,000 shares of common stock outstanding on 1 January 2021, that 20,000 shares were issued for cash on April 1, 2021, and that 12,000 shares were retired on 1 September 2021. The below table shows the weighted averages shares outstanding calculation in a tabular format. In case there is a large difference between basic and diluted EPS, investors should be aware of the possible increase in the number of shares outstanding in the future. On the other hand, while calculating the dilutive EPS, the denominator includes all possible conversions that can take place and increase the number of shares held by parties.
What is the formula for weighted average shares outstanding?
Earnings per share is a measure of a company’s valuation, calculated by dividing its profit by the number of shares outstanding. A company’s market capitalization is the current market value of all of its outstanding shares. Basic EPS uses outstanding shares, which are actually held by the public and company insiders. These shares are non-dilutive because they do not include any options section 1256 contracts or securities that can be converted. To achieve a proper and fair view of the changes in the number of shares and for the calculation of EPS, the method of weighted average shares outstanding is used. A company may authorize buying back some of its own shares in the market if they believe that the market is undervaluing them and there is enough cash on the balance sheet to do so.
A clearer picture of earnings
- If you have a question about the calculator’s operation, please enter your question, your first name, and a valid email address.
- There is no specific formula, the calculation needs to be done by hand or with a computer program.
- A company may announce a stock split to increase the affordability of its shares and grow the number of investors.
- If the calculator is narrow, columns of entry rows will be converted to a vertical entry form, whereas a wider calculator will display columns of entry rows, and the entry fields will be smaller in size …
It can split its stock to reward its current investors and to make its price per share more tempting to new investors. It can reverse-split its stock to keep its head above water, artificially increasing its share price. It also may coincide with the conversion of stock options awarded to company outsiders into stock shares.
Basic EPS = Basic Weighted Average Shares
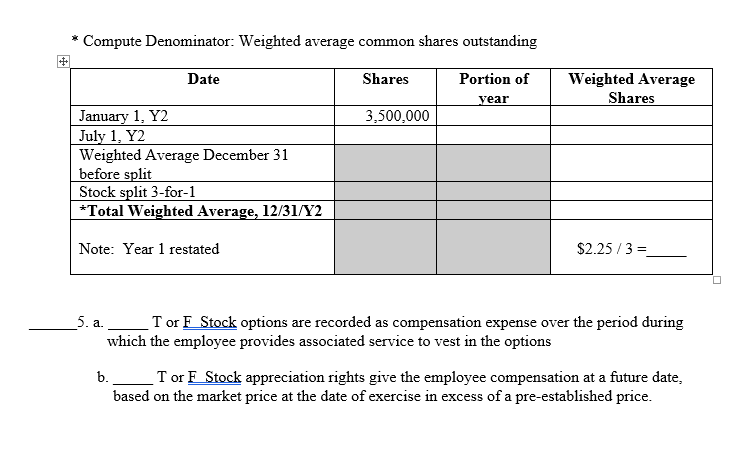
It means that any additional shares issued as a result of stock dividend or split are assumed to be outstanding since the beginning of the year. The weighted average shares outstanding, or the weighted average of outstanding shares, is a calculation that takes into consideration any changes in the number of outstanding shares over a specific reporting period. Investors, when investing for the long term, often compile a position in a stock over several years. Stock prices change daily and keeping track of the cost basis of shares accumulated over many years is desirable. A company may issue new shares to investors or buy its own shares from them during a period. Every time a company issues or repurchases shares, the total number of its outstanding shares changes.
Reverse Stock Split
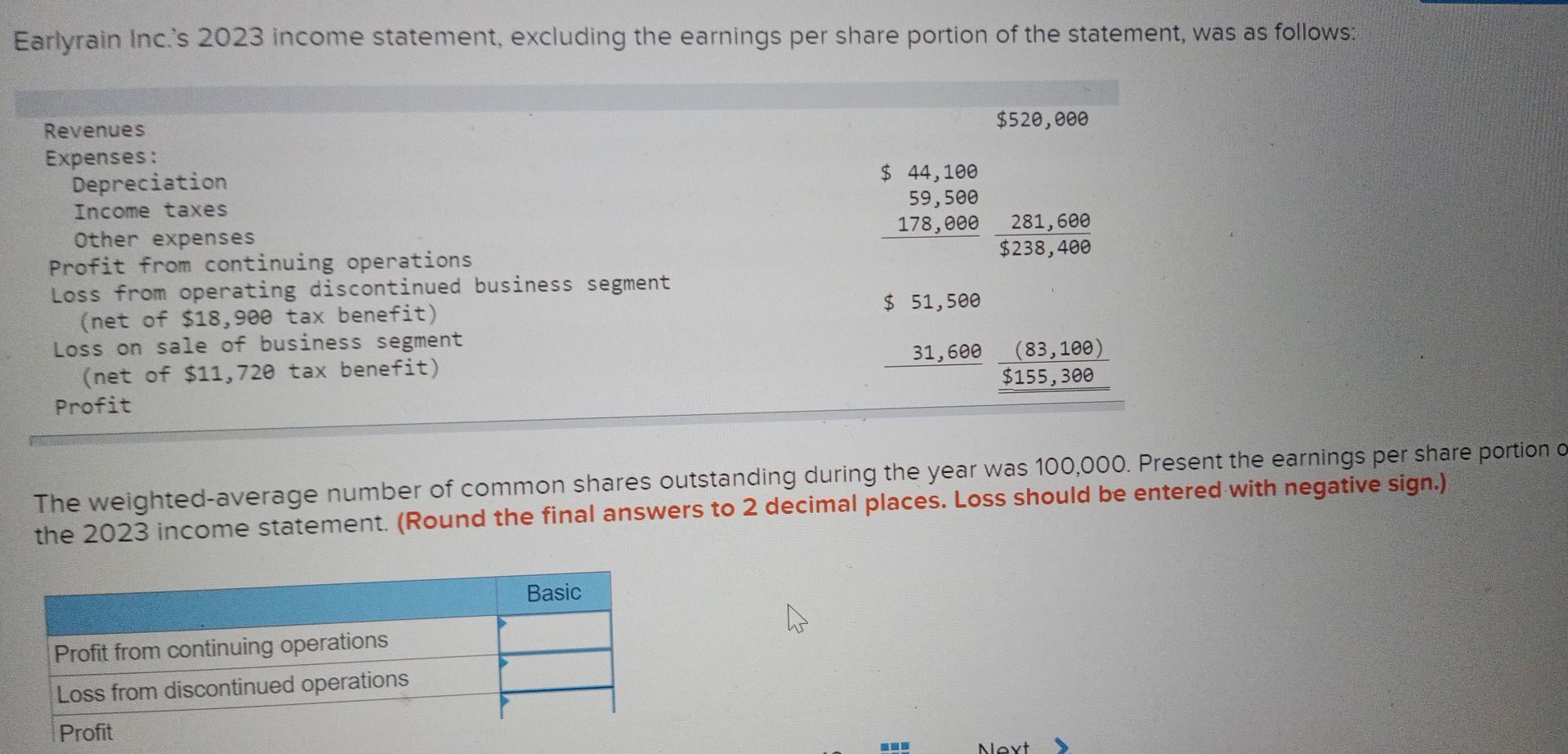
However, a stock dividend or split does have the effect of creating a new “type” of common share in the sense that the percentage of ownership per share is altered. However, the case changes whenever the Company does a stock split or a share reverse. We multiplied the number by 12 for each month and did an average over these 12 months. Since no new shares were issued in this case, each month had 100 thousand shares outstanding; hence, the Company had 1 thousand shares outstanding over the year. Let us consider the following example and incorporate various scenarios that can affect the weighted average number of shares outstanding.
Outstanding shares can also be used to calculate some key financial metrics, including a company’s market cap and its earnings per share. They are separate from treasury shares, which are held by the company itself. Typically, a stock split occurs when a company is aiming to reduce the price of its shares. When this takes place, a company’s outstanding shares increase, and a higher degree of liquidity results. By contrast, a reverse stock split occurs when a company seeks to elevate its share price. Often, a company does this to meet listing requirements, which often require a minimum share price.
This number is significantly important for public companies as it constitutes the basis for computing important financial metrics like earnings per share (EPS). Since private companies are not legally required to report EPS on their income statement, they don’t need to calculate the weighted average number of shares outstanding. Basic weighted average shares, on the other hand, represents the above-mentioned weighted average shares outstanding less the dilution of stock options for a specific period. Dilution occurs when a company issues additional shares that reduce an existing investor’s proportional ownership in the company. The stock dividend and stock split both affect the computation of weighted average shares outstanding for a period. When a company issues a stock dividend or exercises a stock split, it needs to restate its outstanding shares of common stock before the date of stock dividend or split to compute its weighted average number of shares.
Of course, merely increasing the number of outstanding shares is no guarantee of success; the company has to deliver consistent earnings growth as well. To most accurately reflect its earnings per share, we need to know how many shares there were during the entire period — not just at the end. To do this, we need to calculate a weighted average of the company’s outstanding shares over the time period. The following results from the calculator on this page show how the weighted average calculation more accurately reflects the day-to-day average of outstanding shares. A company’s outstanding shares may change over time because of several reasons.
